Pharmaceutical intermediates are organic compounds essential to the synthesis of drugs, either as precursors or derivatives of APIs, or directly as pharmaceutical agents. These fine chemicals, which do not require a drug production license and can be produced in standardized plants, play a vital role in the drug development process. They are classified according to their application areas, such as antibiotics, analgesics, or anticancer intermediates, and specific product types, including cephalosporin and vitamin intermediates. Pharmaceutical intermediates have the characteristics of stability, activity, and controllability, which can improve the efficiency of drug synthesis while helping to reduce production costs. With the increasing severity of global health issues and the aging population, the demand for these intermediates is rising, driven by technological innovations aimed at improving production efficiency and product quality. They are crucial in both the production of APIs and the research and development of new drugs to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the final drug.
Get Consultation
L-Lysine, chemically known as 2,6-diaminohexanoic acid, is a vital essential amino acid required for human and mammalian growth and health.
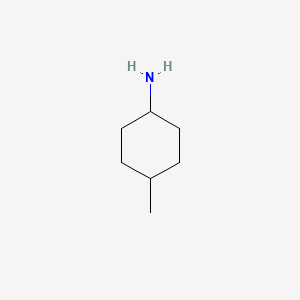
Cis-4-Methylcyclohexylamine (CAS: 2523-56-0) is an organic amine characterized by its molecular formula C7H15N and a molecular weight of 113.201.



